Cellular stress promotes inflammation via sphingosine-1-phosphate
The photo prints are only free of charge if a report is being written about the university.
Please use the reference: University of Hohenheim or the source mentioned below the picture
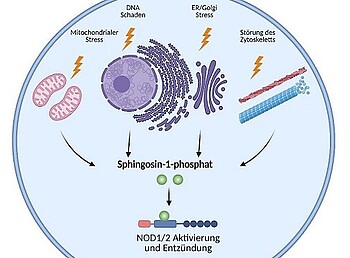
Picture Credit: The Authors | Cellular stress induces inflammatory responses; however precise mechanisms remain unknown. We show that various stimuli, including disruption of cytoskeleton, ER stress, Golgi stress, mitochondrial stress or DNA damage, all converge in the accumulation of the endogenous lipid metabolite sphingosine-1-phosphate in the cytosol. Subsequently, sphingosine-1-phosphate binds to and activates NOD1/2 resulting in inflammatory responses.
