Impact of Na+ -translocating NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (NQR) on iron uptake and nqrM expression in Vibrio cholerae
The photo prints are only free of charge if a report is being written about the university.
Please use the reference: University of Hohenheim or the source mentioned below the picture
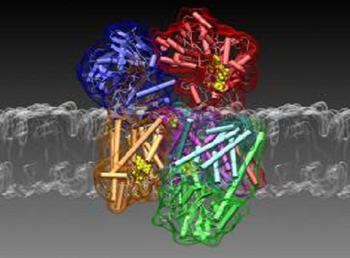
The Na+ -translocating NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (NQR) generates an electrochemical Na+ gradient in vivo which is crucial for expulsion of bactericidal drugs by secondary efflux systems. Moreover, this respiratory Na+ pump is the major catabolic NADH dehydrogenase required for the regeneration of NAD+. Electrons are delivered to ubiquinone (Q) which is reduced to ubiquinol (QH2), a substrate for downstream respiratory complexes.
