Oncostatin M reguliert die Produktion des Fibroblasten-Wachstumsfaktors 23 (FGF23) in osteoblastenähnlichen Zellen [18.08.23]
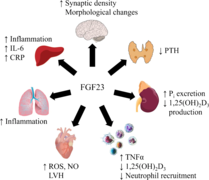
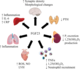
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) ist ein Protein, welches zusammen mit seinem essentiellen Cofaktor Klotho eine wichtige Rolle im Phosphatstoffwechsel spielt. Während verminderte Klotho- und FGF23-Spiegel Alterungserscheinungen verstärken, beobachtet man die Erhöhung der Konzentration von FGF23 im Plasma z.B. bei Niereninsuffizienzen, Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen und auch bei onkogenen Knochenerkrankungen. Die Steuerungsmechanismen der FGF23-Produktion sind daher für die Diagnose und Behandlung dieser Erkrankungen von großem Interesse. Eine aktuelle Studie der Arbeitsgruppe von Prof. Michael Föller untersucht, welche regulierende Rolle Oncostatin M als Mitglied der IL-6 Zytokinfamilie für die Produktion von FGF23 in Osteoblasten-ähnlichen Zellen spielt.Originalpublikation
Münz S., Feger M., Föller M. (2023) Oncostatin M is a regulator of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) in UMR106 osteoblast-like cells. Scientific Reports, 13 (1), art. no. 8420, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34858-6
ABSTRACT
Renal phosphate and vitamin D metabolism is under the control of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), an endocrine and paracrine factor predominantly produced in bone. FGF23 formation is stimulated by active vitamin D, or parathyroid hormone (PTH), which are further regulators of phosphate homeostasis. In renal, inflammatory, and other diseases, plasma FGF23 reflects disease stage and correlates with outcome. Oncostatin M is part of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) family and regulates remodeling and PTH effects in bone as well as cardiac FGF23 production in heart failure via glycoprotein gp130. Here, we studied whether oncostatin M is a regulator of FGF23 in bone cells. Experiments were performed in UMR106 osteoblast-like cells, Fgf23 mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR, FGF23 protein by Western Blotting and ELISA, and oncostatin M receptor and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) receptor gene knockout accomplished by siRNA. As a result, oncostatin M dose-dependently up-regulated Fgf23 expression and protein secretion. The oncostatin M effect on FGF23 was mediated by oncostatin M receptor and gp130 and involved, at least in part, STAT3 and MEK1/2. Taken together, oncostatin M is a regulator of FGF23 through oncostatin M receptor, gp130, as well as STAT3 and MEK1/2 in UMR106 osteoblasts. © 2023, The Author(s).
Diese Studie wurde durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG, Fo 695/2-2 gefördert. All Open Access wird im Rahmen des Projektes DEAL ermöglicht.
Kontakt zum Autor
 | Professor Dr. Michael FöllerTel: +49 711 459 24566 physiologie(at)uni-hohenheim.de |