In vitro manipuliertes Fettgewebe für Behandlung und Pharma-Screening [05.03.18]
Fettgewebe ist sehr gefragt, um verlorenes oder geschädigtes Weichgewebe zu behandeln oder um z.B. die Effekte von neuen Medikamenten zu studieren. Heutzutage sind die meisten dieser Pharma-Tests abhängig von Tier-Seren. Eine Hohenheim-Reutlinger Forscher-Tandem hat ein in vitro Fettgewebe-Testsystem entwickelt, das seine Funktionalität ohne die Zugabe von Seren langfristig aufrechterhalten kann.Originalpublikation in Cytotherapy, March 2018:
Completely serum-free and chemically defined adipocyte development and maintenance
1 Reutlingen Research Institute, Reutlingen University, Reutlingen Germany
2 University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany
3 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB, Stuttgart, Germany
Methods
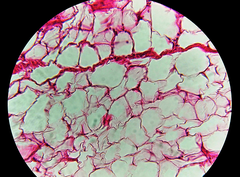
Human adipose tissue–derived stem cells were expanded and characterized in a xeno- and serum-free environment. Adipogenic differentiation was induced using a completely defined medium. Developed adipocytes were maintained in a completely defined maturation medium for additional 28 days. In addition to cell viability and adherence, adipocyte-specific markers such as perilipin A expression or leptin release were evaluated.
Results
The defined differentiation medium enhanced cell adherence and lipid accumulation at a significant level compared with the corresponding negative control. The defined maturation medium also significantly supported cell adherence and functional adipocyte maturation during the long-term culture period.
Conclusions
The process described here enables functional adipocyte generation and maintenance without the addition of unknown or animal-derived constituents, achieving an important milestone in the introduction of adipose tissue–engineered products into clinical trials or in vitro screening.